Identifying and Correcting Gingivitis
Gingivitis causes gum inflammation, redness, and bleeding. Poor oral hygiene, plaque buildup, and gum irritation trigger gingivitis. If untreated, gingivitis leads to periodontitis and tooth loss. Early detection and proper treatment reverse gingivitis and restore gum health. Brushing, flossing, and professional cleanings reduce plaque and inflammation. Understanding the signs of gingivitis helps prevent long-term damage. Treating gingivitis early strengthens gums and improves dental comfort. Let’s explore how to identify and correct gingivitis for a healthier smile.
Signs and Symptoms of Gingivitis
Gingivitis causes red, painful, swollen, and bleeding gums. Bleeding while brushing or flossing signals gum inflammation. Gum tenderness increases sensitivity to hot, cold, and sweet foods. Persistent bad breath (halitosis) results from plaque buildup and bacterial growth. Gums may appear shiny or darker in color. Receding gums create gaps where plaque and bacteria collect. Increased plaque and tartar buildup along the gumline worsen inflammation. Gum sensitivity and discomfort increase chewing and speaking difficulty. Untreated gingivitis causes deeper gum pockets and loose teeth. Early detection of symptoms allows for faster treatment and recovery. Identifying gingivitis early reduces gum damage and improves dental health.
Causes of Gingivitis
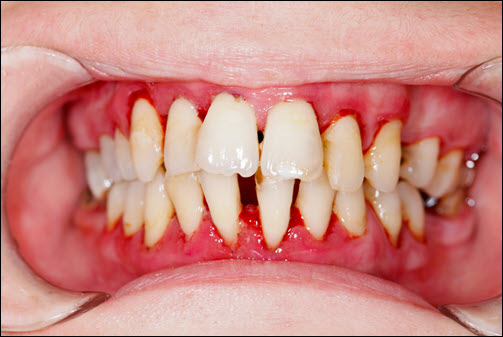 Poor oral hygiene allows plaque to build up along the gumline. Plaque contains bacteria that produce acid, irritating gum tissue. Improper brushing and flossing leave plaque behind, increasing inflammation. Smoking reduces blood flow to gums, slowing healing and increasing sensitivity. Hormonal changes during pregnancy and menopause increase gum sensitivity and inflammation. Misaligned teeth create hard-to-reach areas where plaque collects. Poor diet increases plaque formation and weakens gum tissue. Certain medications reduce saliva flow, increasing dry mouth and plaque buildup. Stress weakens the immune system, reducing gum resistance to bacteria. Identifying the cause of gingivitis improves treatment success. Treating underlying causes strengthens gum health and reduces inflammation.
Poor oral hygiene allows plaque to build up along the gumline. Plaque contains bacteria that produce acid, irritating gum tissue. Improper brushing and flossing leave plaque behind, increasing inflammation. Smoking reduces blood flow to gums, slowing healing and increasing sensitivity. Hormonal changes during pregnancy and menopause increase gum sensitivity and inflammation. Misaligned teeth create hard-to-reach areas where plaque collects. Poor diet increases plaque formation and weakens gum tissue. Certain medications reduce saliva flow, increasing dry mouth and plaque buildup. Stress weakens the immune system, reducing gum resistance to bacteria. Identifying the cause of gingivitis improves treatment success. Treating underlying causes strengthens gum health and reduces inflammation.
Proper Brushing Technique to Treat Gingivitis
Brushing properly removes plaque and reduces gum inflammation. Use a soft-bristled toothbrush and fluoride toothpaste. Hold the toothbrush at a 45-degree angle to the gumline. Brush using small, circular motions to clean all tooth surfaces. Clean the front, back, and chewing surfaces of each tooth. Brush for at least two minutes, twice a day. Avoid scrubbing too hard to prevent gum damage. Clean the tongue and roof of the mouth to remove bacteria. Replace the toothbrush every three months or when bristles fray. Electric toothbrushes improve plaque removal and increase brushing efficiency. Proper brushing reduces plaque buildup and improves gum health.
Flossing to Remove Plaque Between Teeth
Flossing removes plaque and bacteria from between teeth and under the gumline. Use about 18 inches of floss, wrapping it around your middle fingers. Slide the floss gently between teeth using a back-and-forth motion. Curve the floss into a “C” shape around each tooth. Clean under the gumline without snapping the floss to avoid gum damage. Use a clean section of floss for each tooth to prevent bacteria transfer. Water flossers and floss picks provide alternative methods for tight spaces. Flossing reduces plaque buildup and improves gum health. Clean gumlines reduce sensitivity and inflammation. Consistent flossing strengthens gum attachment and improves overall comfort.
Using Antibacterial Mouthwash to Reduce Inflammation
Antibacterial mouthwash reduces plaque and gum inflammation. Use a fluoride or alcohol-free mouthwash to protect gum tissue. Pour about 20 milliliters of mouthwash into a cup. Swish it around your mouth for 30 to 60 seconds. Gargle to clean the back of the throat and remove bacteria. Spit out the mouthwash and avoid rinsing with water afterward. Antiseptic mouthwash reduces plaque buildup and gum sensitivity. Alcohol-free mouthwash prevents dry mouth and improves gum moisture. Regular mouthwash use reduces gum bleeding and inflammation. Clean gums improve tooth stability and bite strength. Antibacterial mouthwash strengthens gum health and reduces gingivitis risk.
Professional Dental Cleaning to Remove Tartar
 Dentists remove tartar and plaque that brushing and flossing miss. Professional cleaning (scaling) removes hardened plaque from tooth surfaces and gum pockets. Dentists use ultrasonic tools to loosen tough tartar and improve gum health. Deep cleaning (scaling and root planing) smooths tooth roots and reduces gum inflammation. Professional fluoride treatments strengthen enamel and reduce sensitivity. Regular cleanings every six months improve plaque removal and gum strength. Professional monitoring detects early signs of gingivitis and gum disease. Treating gingivitis early prevents bone loss and tooth shifting. Professional dental care improves overall gum health and tooth stability. Clean gums increase comfort and dental confidence.
Dentists remove tartar and plaque that brushing and flossing miss. Professional cleaning (scaling) removes hardened plaque from tooth surfaces and gum pockets. Dentists use ultrasonic tools to loosen tough tartar and improve gum health. Deep cleaning (scaling and root planing) smooths tooth roots and reduces gum inflammation. Professional fluoride treatments strengthen enamel and reduce sensitivity. Regular cleanings every six months improve plaque removal and gum strength. Professional monitoring detects early signs of gingivitis and gum disease. Treating gingivitis early prevents bone loss and tooth shifting. Professional dental care improves overall gum health and tooth stability. Clean gums increase comfort and dental confidence.
Improving Diet and Nutrition to Strengthen Gums
A balanced diet strengthens gum tissue and reduces inflammation. Calcium-rich foods like milk, cheese, and yogurt improve enamel strength. Leafy greens and crunchy vegetables increase saliva flow and clean teeth naturally. Vitamin C (found in citrus fruits) strengthens gum tissue and reduces bleeding. Avoid sugary and acidic snacks that increase plaque buildup and gum irritation. Drinking water throughout the day improves saliva production and gum hydration. Nuts and seeds provide essential minerals for gum strength. Better nutrition reduces inflammation and improves gum health. Stronger gums improve tooth stability and bite comfort. A balanced diet supports overall dental health and strength.
Avoiding Harmful Habits to Protect Gums
Smoking weakens gum tissue and increases plaque buildup. Nicotine reduces blood flow to gums, slowing healing and increasing inflammation. Quitting smoking improves gum attachment and reduces gum recession. Grinding and clenching place pressure on gums and weaken attachment. Wearing a night guard protects teeth and gums from grinding pressure. Avoid biting on hard objects like ice and pens to prevent gum injury. Reducing alcohol intake prevents dry mouth and plaque buildup. Proper hydration improves gum strength and reduces sensitivity. Better daily care reduces gum inflammation and improves tooth support. Avoiding harmful habits strengthens gum health and dental comfort.
Monitoring Gum Health with Regular Dental Visits
Dentists monitor gum health and detect early signs of gingivitis. Professional cleanings remove plaque and tartar from hard-to-reach areas. Dentists measure gum pocket depth to check for inflammation and tissue loss. Early detection of gum disease improves treatment success and reduces damage. Regular fluoride treatments strengthen enamel and reduce sensitivity. Professional scaling and root planing reduce plaque and gum inflammation. Consistent monitoring improves gum attachment and bite strength. Regular dental checkups reduce the need for complex treatments. Improved gum health increases tooth stability and overall comfort. Professional care strengthens long-term dental health and confidence.
Gingivitis causes gum inflammation, bleeding, and sensitivity. Early detection prevents gum disease and tooth loss. Proper brushing and flossing reduce plaque and improve gum health. Antibacterial mouthwash reduces bacteria and strengthens gum tissue. Professional cleanings remove tartar and prevent gum recession. A balanced diet strengthens gums and reduces inflammation. Avoiding harmful habits protects gum health and reduces sensitivity. Regular dental checkups detect early signs of gingivitis and improve treatment success. Investing in gum health improves long-term dental strength and comfort. Stronger gums and healthier teeth increase confidence and smile strength.